Big Data represents the massive volumes of structured and unstructured information generated daily across industries. Understanding its five key characteristics and technological foundations is crucial for organizations seeking to harness data-driven insights for competitive advantage and innovation.
The Five Vs Framework
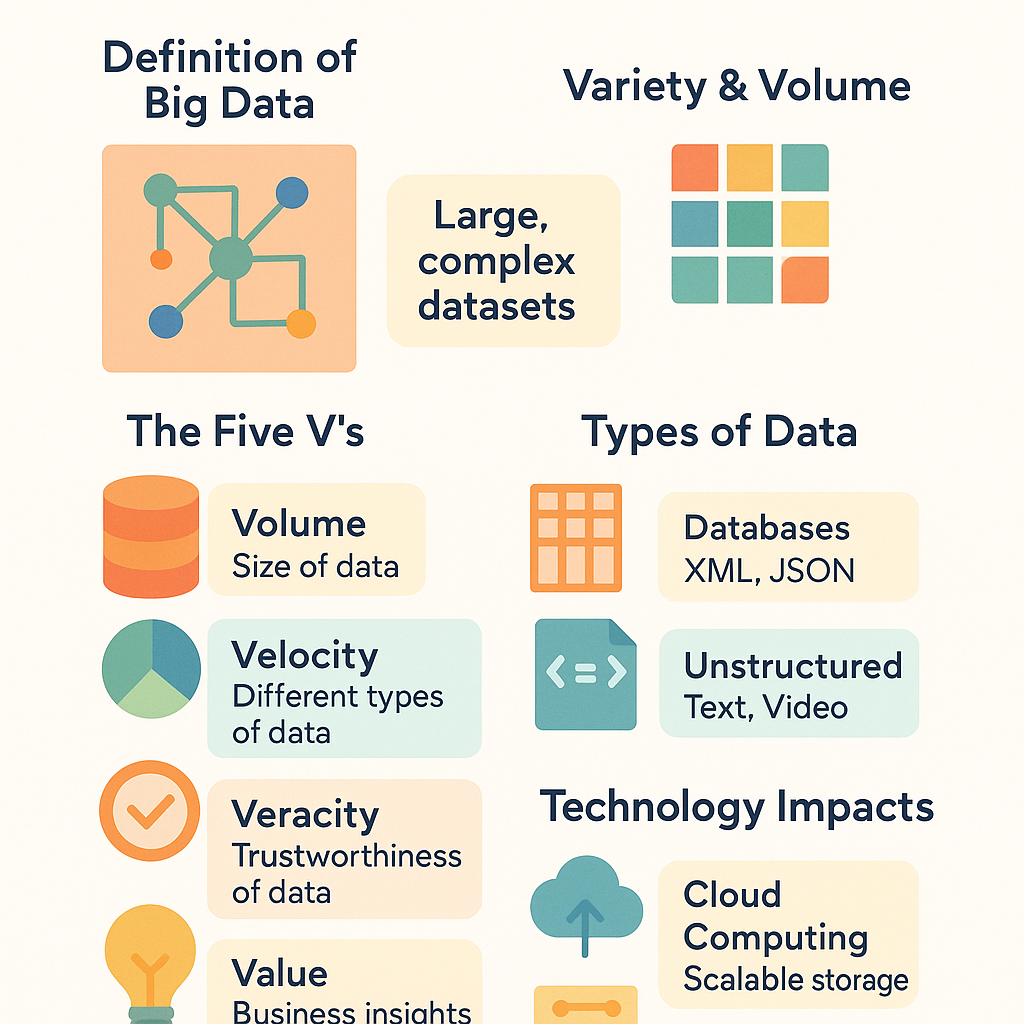
Big Data is characterized by five essential dimensions: Volume (massive data quantities), Velocity (high-speed data generation), Variety (diverse data formats), Veracity (data accuracy and reliability), and Value (meaningful insights extraction). This framework helps organizations understand and manage complex data ecosystems effectively.
Understanding Big Data
Big data represents a fundamental shift from traditional data management approaches, characterized by datasets so large and complex that conventional processing tools cannot handle them effectively. While traditional data typically involves structured information stored in relational databases with predictable formats, big data encompasses vast collections of diverse information generated at unprecedented speeds from multiple sources including social media, sensors, transactions, and digital interactions.
The Five Vs Framework
The evolution of big data analysis relies on understanding five critical characteristics that distinguish it from conventional data processing. Volume refers to the massive scale of information generated daily, with organizations now managing petabytes of data compared to the gigabytes of traditional systems. Modern businesses process exponentially larger datasets that require distributed storage solutions and parallel processing capabilities to extract meaningful insights.
Velocity describes the unprecedented speed at which data flows into organizational systems. Real-time processing has become essential as streaming data from IoT devices, financial transactions, and social media platforms demands immediate analysis for competitive advantage. This rapid data generation necessitates advanced processing architectures capable of handling continuous information streams without bottlenecks.
Variety and Quality Considerations
Variety encompasses the diverse formats of modern data, including structured databases, semi-structured logs, and unstructured content like videos, images, and text documents. Organizations must integrate disparate data types to create comprehensive analytical frameworks that provide holistic business insights.
Veracity addresses data quality and accuracy challenges inherent in large-scale information collection. With multiple sources contributing to big data repositories, ensuring reliability through validation processes and error detection becomes crucial for meaningful analysis. Value represents the ultimate goal of extracting actionable insights that drive strategic business decisions and operational improvements.
Technological Enablers
Cloud computing and machine learning advancements have revolutionized big data processing capabilities. Distributed computing platforms enable organizations to scale analytics operations dynamically, while sophisticated algorithms can identify patterns within complex datasets that would be impossible to detect through traditional methods. These technological innovations have democratized big data analytics, making advanced processing accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Technologies Behind Big Data
The technological landscape supporting Big Data has evolved dramatically over the past decade, with cloud-based solutions emerging as the dominant force in data management and analysis. Major technology providers have developed comprehensive platforms that enable organizations to process, store, and analyze massive datasets with unprecedented efficiency and scale.
Cloud Infrastructure and Platform Solutions
Amazon Web Services (AWS) leads the market with its extensive suite of Big Data services, including Amazon EMR for managed Hadoop clusters and Amazon Redshift for data warehousing. The platform processes over 100 exabytes of data monthly across its global infrastructure, demonstrating the massive scale of modern data operations. Google Cloud Platform offers BigQuery, which can analyze petabytes of data in seconds, while Microsoft Azure provides HDInsight and Azure Data Factory for comprehensive data pipeline management.
These cloud platforms have fundamentally transformed data storage economics, reducing costs by up to 70% compared to traditional on-premises solutions while providing virtually unlimited scalability. Organizations can now provision computing resources dynamically, paying only for actual usage rather than maintaining expensive hardware infrastructure.
Open Source Frameworks and Enterprise Solutions
Hadoop remains a cornerstone technology, with its distributed file system enabling organizations to store and process large datasets across commodity hardware clusters. Apache Spark has gained significant traction for real-time analytics, processing data up to 100 times faster than traditional MapReduce operations. IBM’s Watson platform leverages advanced machine learning algorithms and natural language processing (NLP) capabilities to extract insights from unstructured data sources.
Specialized Analytics Platforms
SAS continues to provide enterprise-grade statistical analysis tools, particularly valuable for predictive modeling and advanced analytics workflows. Oracle’s Big Data Cloud Service integrates seamlessly with existing enterprise databases, while offering specialized tools for IoT data processing. These platforms support organizations in managing the complexity of multi-format data streams from sensors, social media, and transactional systems.
The convergence of these technologies has enabled real-time decision-making capabilities that were previously impossible, transforming how organizations approach data-driven strategy and operational efficiency.

Applications of Big Data Across Industries
The transformative power of Big Data extends across virtually every sector of the modern economy, revolutionizing how organizations operate, make decisions, and serve their customers. From healthcare providers analyzing patient outcomes to financial institutions detecting fraudulent transactions, Big Data applications have become integral to competitive advantage and operational excellence.
Healthcare Revolution Through Data Analytics
Healthcare stands as one of the most impactful domains for Big Data implementation, where patient lives depend on accurate, timely information processing. Medical institutions leverage vast datasets from electronic health records, IoT-enabled medical devices, and genomic sequencing to deliver personalized treatment plans. Real-time monitoring systems process data from wearable devices, allowing healthcare providers to detect anomalies in patient vital signs before critical situations develop. According to recent studies, predictive analytics in healthcare can reduce readmission rates by up to 30% while improving patient satisfaction scores significantly.
Financial Services and Risk Management
The finance sector has embraced Big Data technologies to enhance risk assessment, fraud detection, and customer service delivery. Banks process millions of transactions daily through platforms hosted on Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud, analyzing patterns to identify suspicious activities within milliseconds. Credit scoring algorithms now incorporate alternative data sources, including social media activity and mobile phone usage patterns, providing more comprehensive risk profiles. Investment firms utilize Hadoop clusters to process market data, news feeds, and economic indicators simultaneously, enabling algorithmic trading strategies that respond to market conditions in real-time.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Optimization
Manufacturing industries have transformed their operations through IoT sensors and predictive maintenance systems powered by Big Data analytics. Oracle and IBM solutions enable manufacturers to monitor equipment performance continuously, predicting failures before they occur and reducing downtime by up to 50%. Supply chain optimization algorithms process data from multiple sources, including weather patterns, transportation networks, and supplier performance metrics, to minimize costs and improve delivery times.
Government and Public Policy Innovation
Government agencies increasingly rely on Big Data for evidence-based policy making and public service improvement. Smart city initiatives utilize data from traffic sensors, environmental monitors, and citizen feedback platforms to optimize urban planning and resource allocation. Emergency response systems integrate real-time data from multiple sources to coordinate disaster relief efforts more effectively, potentially saving thousands of lives during natural disasters.

Future Opportunities and Challenges in Big Data
The trajectory of big data continues to evolve rapidly, presenting unprecedented opportunities alongside complex challenges that organizations must navigate strategically. As we advance into 2025 and beyond, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies with big data systems promises to unlock new levels of analytical sophistication and operational efficiency.
Technological Evolution and AI Integration
The convergence of big data with advanced AI technologies is reshaping how organizations extract value from their information assets. Machine learning algorithms are becoming increasingly sophisticated in processing vast datasets, enabling real-time analytics that were previously impossible. Data science teams are leveraging these capabilities to develop predictive models that can anticipate market trends, customer behaviors, and operational challenges with remarkable accuracy. Amazon Web Services and similar cloud platforms are continuously expanding their AI-powered analytics offerings, making these advanced capabilities accessible to organizations of all sizes.
The future landscape will likely see the emergence of autonomous data systems that can self-optimize and adapt without human intervention. These systems will utilize advanced neural networks to identify patterns across multiple data streams simultaneously, providing insights that traditional analytical approaches cannot achieve.
Regulatory Compliance and Data Privacy Challenges
As big data applications expand, regulatory frameworks are becoming increasingly stringent. HIPAA compliance remains a critical concern for healthcare organizations handling patient data, requiring sophisticated encryption and access control mechanisms. Organizations must invest heavily in compliance infrastructure to meet evolving regulatory requirements while maintaining operational efficiency.
Data privacy concerns are intensifying as consumers become more aware of how their information is collected and utilized. Companies must balance the need for comprehensive data collection with respect for individual privacy rights, implementing transparent data governance policies that build trust while enabling innovation.
Workforce Development and Skills Gap
The growing demand for skilled data science professionals presents both an opportunity and a challenge. Organizations must invest in training programs and talent acquisition strategies to build teams capable of managing complex big data initiatives effectively.

What to remember about Big Data’s future impact
Big Data continues to evolve as a transformative force across industries, driven by advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning integration. Organizations must prepare for emerging challenges including data privacy regulations and the growing demand for skilled professionals. The convergence of cloud computing, IoT, and advanced analytics will create new opportunities for innovation while requiring robust compliance frameworks and strategic planning for sustainable data-driven growth.